If f (x) = x1/x1 then find the value of f (2x) Find the answer to this question along with unlimited Maths questions and prepare better for JEE examinationGet answer If f_(r)(x),g_(r)(x),h_(r)(x),r=1,2,3 are polynomials in x such that f_(r)(a)=g_(r)(a)=h_(r)(a),r=1,2,3 and F(x)=(f_(1)(x),f_(2)(x),f_(3)(x)),(g_(1)(x),gIf f(x) x^2f(x)^3 = 10 and f(1) = 2, find f'(1) 🎉 Announcing Numerade's $26M Series A, led by IDG Capital!Read how Numerade will revolutionize STEM Learning Books;

Ex 1 3 8 F X X2 4 Show That F Is Invertible Chapter 1
If f^2(x).f(1-x/1 x)=x^3
If f^2(x).f(1-x/1 x)=x^3-Assuming that f is nonzero, we can rewrite this equation as 1 f(x) 1 f(1 / x) = 1 Making the substitution g(y) = − 1 2 1 f ( ey), we get the functional equation g(y) g( − y) = 0, which simply says that g is odd This equation can be solved, with the initial condition, by setting g(y) = cy for a suitable constant cGet answer If f_(n)(x),g_(n)(x),h_(n)(x),n=1, 2, 3 are polynomials in x such that f_(n)(a)=g_(n)(a)=h_(n)(a),n=1,2,3 and F(x)={(f_(1)(x),f_(2)(x),f_(3)(x)),(g_(1




How Do You Find A Quadratic Function F X Ax 2 Bx C For Which F 1 2 F 3 46 And F 3 16 Socratic
M 2, and M 3 be metric spaces Let gbe a uniformly continuous function from M 1 into M 2, and let fbe a uniformly continuous function from M 2 into M 3 Prove that f gis uniformly continuous on M 1 Solution Let >0 Since fis uniformly continuous, there exists some >0 such that d 2(x;y) < implies d 3(f(x);fSimple and best practice solution for f(x)=2(x1)(x3) equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve itSolve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more
2 Nullstellen bei x =1, x =1 Extrema Minimum ( 1 0 ), Maximum ( 1/3 1,1851 ) Wendepunkte Wendepunkt ( 1/3 16/27 ) Skizze siehe unten b) Bestimme dieExamples 8 • f(x) = x31 2 xisonetoone, since f0(x) = 3x2 1 2 > 0 for all x • f(x) = −x5−2x3−2xisonetoone, since f0(x) = −5x4 −6x2 −2 < 0 for all x • f(x) = x−πcosxisonetoone, since f0(x) = 1−sinx ≥ 0 and f0(x) = 0 only at x = π 2 2kπ 2 Inverse Functions 21 Definition of Inverse Functions What are Inverse Functions? If f(x)x^33x2 find f(1) Ask your question ver09 ver09
It has been provided or mentioned that a function F(x1)=x^2–3x2 Interestingly, if we substitute a value of x1 in the place of x, we obtain, F((x1)1)=F(x) Therefore, F(x)=(x1)^2–3(x1)2=x^2–2x1–3x32=x^2–5x6 Hence, the function F(x) canAnd it must be 3 mod 4 because f 2 (4n 1) = 3n 1, smaller than 4n 1 For each starting value a which is not a counterexample to the Collatz conjecture, there is a k for which such an inequality holds, so checking the Collatz conjecture for one starting value is as good as checking an entire1)if x kilograms of rice costs 84y pesos, how much would m kilograms cost?



Madasmaths Com Archive Maths Booklets Standard Topics Various Function Exam Questions Pdf




If F X X 1 X 1 Then Prove That F 2x 3f X 1 F X 3 Brainly In
If f^2(x)f(1x/1 x)=x^3Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historySolve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more If F X X 3 X 2f 1 Xf 2 F 3 Then F 2Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music WolframAlpha brings expertlevel knowledge Funktionsuntersuchung f (x) = 1/6 (x1) 2 (x2) für x ∈ ℝ a) Beschreiben Sie den Globalen Verlauf der Funktion f für x → ∞ und für x → – ∞ b) Bestimmen Sie die Nullstellen der Art der Nullstellen, d h ob mit oder ohne Vorzeichenwechsel (VZW) c) Bestimmen Sie die erste und zweite Ableitung von f




Derivatives Of Inverse Functions Video Khan Academy




If F 0 1 F 2 3 F 2 5 And F 0 Is Finite Then Int 0 1 Xf 2x Dx Is Equal To Youtube
¥ 1 x n n = ex = exp (x) Eine Motiv ation für dieseTo ask Unlimited Maths doubts download Doubtnut from https//googl/9WZjCW If` 2f(x)3f(1/x)=x^21` then `f(x)` is I'll do #f(x) = x^3 1# and leave #f(x) = 2x 3# up to you to do for practice The inverse of a function can be found algebraically by switching the values of #x# and #y# inside the function #y = x^3 1# #x = y^3 1# #x 1 = y^3# #root(3)(x 1) = y# Let's now use your trick that this new function is indeed the inverse function




Ex 1 3 8 F X X2 4 Show That F Is Invertible Chapter 1




Mcq Class 12 If F X 3 X 3 1 3 Then Fof X Is Teachoo
Mathf(x1)=2x3/math Let matht=x1\implies x=t1/math math\therefore f(t)=2(t1)3/math mathf(t)=2t5/math matht/math can be replaced by mathx1 Example 1 f(x) = x We'll find the derivative of the function f(x) = x1 To do this we will use the formula f (x) = lim f(x 0 0) Δx→0 Δx Graphically, we will be finding the slope of the tangent line at at an arbitrary point (x 0, 1 x 1 0) on the graph of y = x (The graph of y = x 1 is a hyperbola in the same way that the graph of3 Definition 9 Let f be a oneto
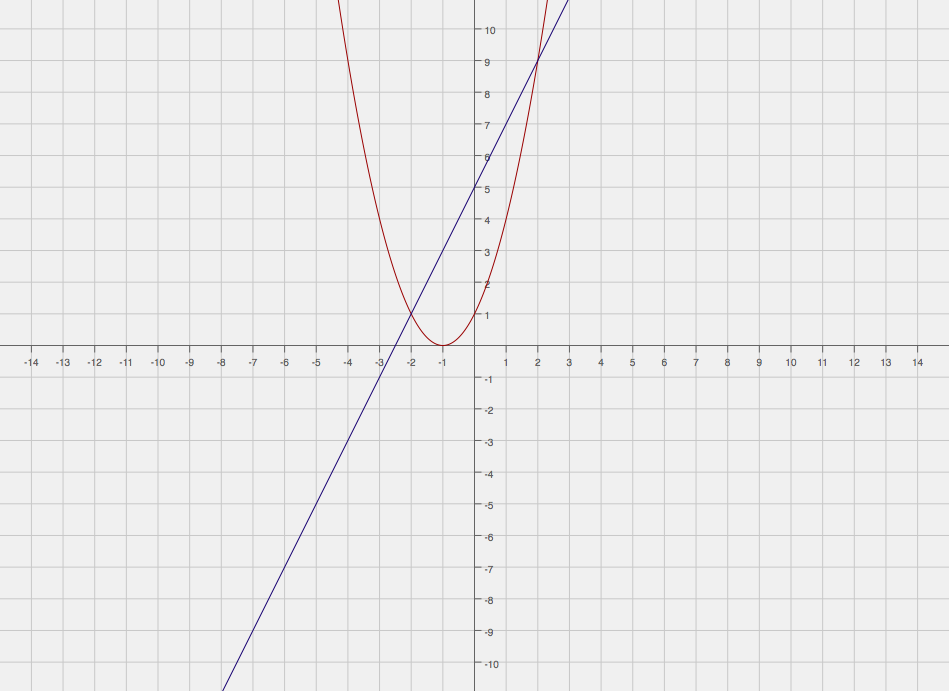



How Do You Find The Area Between F X X 2 2x 1 And G X 2x 5 Socratic
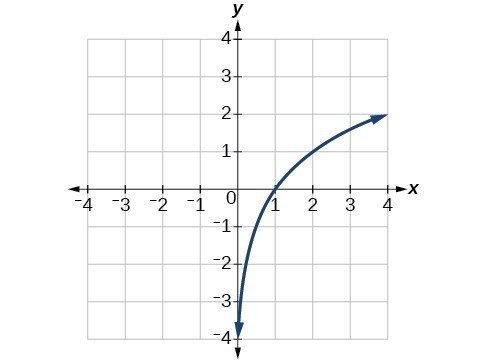



Use The Graph Of A Function To Graph Its Inverse College Algebra
If $f(x) x^2f(x)^3 = 10$ and $f(1) = 2$, find $f '(1)$ I'm not entirely sure how to solve this problem My first instinct would be to plug in a 2 for every $f(xSatz Es gibt genau eine Funktion f mit f0(x) = f(x) f ur alle x 2R und f(0) = 1 Dies ist einleuchtend, sp ater kommen wir auf den Beweis noch einmal zur uck Man schreibt diese Funktion exp(x) und nennt sie die Exponentialfunktion oder eFunktionClick here👆to get an answer to your question ️ \"If \\( f ( x ) = 2 x x , g ( x ) = \\frac { 1 } { 3 } ( 2 x x ) \\) and \\( h ( x ) = f ( g ( x




A Polynomial Function Satisfies F X F 1 X 2f X 2f 1 X If F 2 18 Find F 3 No Links Please Maths Relations And Functions Meritnation Com




Finding Inverse Functions Quadratic Example 2 Video Khan Academy
If X ≠ 1 and F ( X ) = X 1 X − 1 is a Real Function, Then F(F(F(2))) Is(A) 1 (B) 2 3 (D) 4 Department of PreUniversity Education, Karnataka PUC Karnataka Science Class 11 Textbook Solutions 71 Important Solutions 3 Question Bank Solutions 51 Concept Notes & Videos 531 Syllabus Advertisement Remove all ads If X ≠ 1 and F ( X ) = X 1 X − 1 is a Real Function, Then F Find f'(1) if f(x) = ((x 1)/(2x2 7x 5)), when x ≠ 1 f(x) = 1/3, when x = 1 Welcome to Sarthaks eConnect A unique platform where students can interact with teachers/experts/students to get solutions to their queriesFree math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutor




4 2 Linear Approximations And Differentials Mathematics Libretexts



Efisd Net Common Pages Displayfile Aspx Itemid
Find an answer to your question If f(x)= 1/2 x3, find f^1 (x) DemitiAfrorii is waiting for your help Add your answer and earn pointsIf f(x) = x^3 x^2 x 1 Then the value of f ( 1 ) f ( 1 ) / 2 = _____ Get the answers you need, now!Divide f2, the coefficient of the x term, by 2 to get \frac{f}{2}1 Then add the square of \frac{f}{2}1 to both sides of the equation This step makes the left hand side of
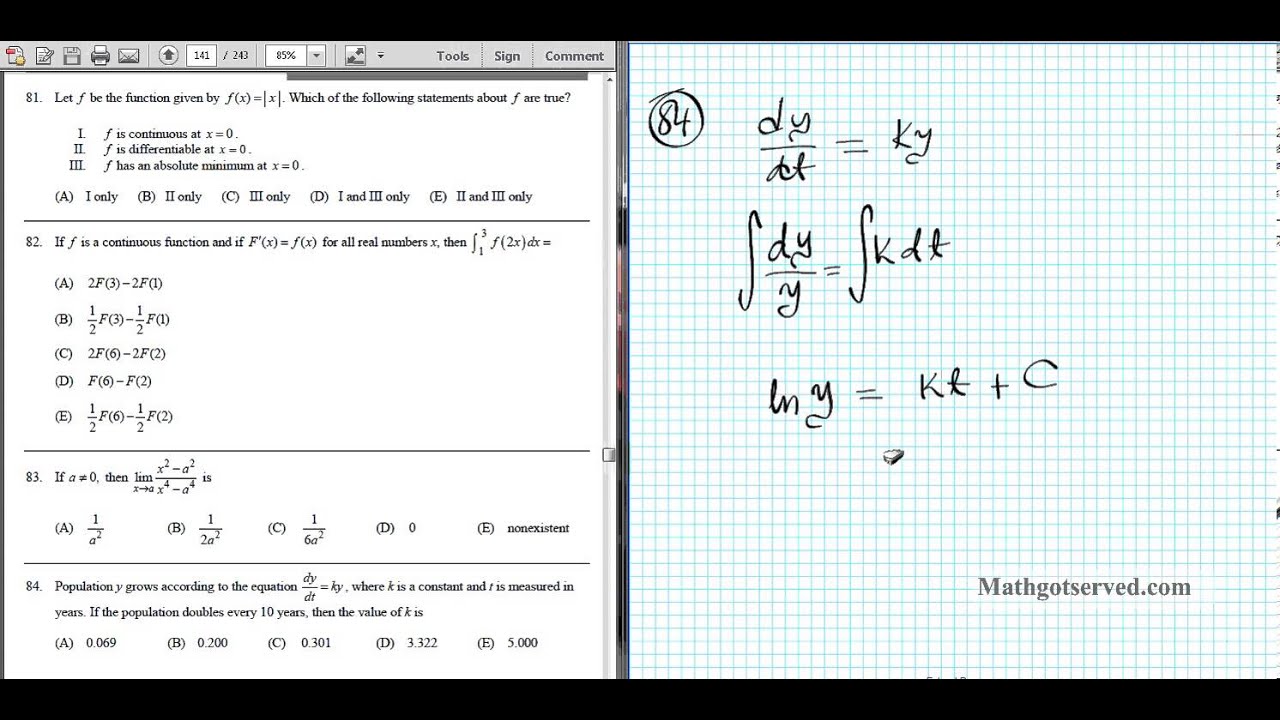



Ap Calculus Ab Multiple Choice 1998 Exam Part B Videos Questions Solutions



If F And G Are Two Real Valued Functions Defined As F X 2x 1 G X X2 1 Then Find Studyrankersonline
Get an answer for 'If f(x) x^(2)f(x)^3= 10 and f(1) = 2, find f'(1)' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotes3 x2 2 >1 This shows that f(x) = x3 is not uniformly continuous on R 445 Let M 1;2)the area of rectangular is (49x²36y²) sq meters find the expression to represent its




If F 2 X F 1 X 1 X X 3 X 1 1 And F X 0 Then Find F 2 Where Is The Greatest Integer Function
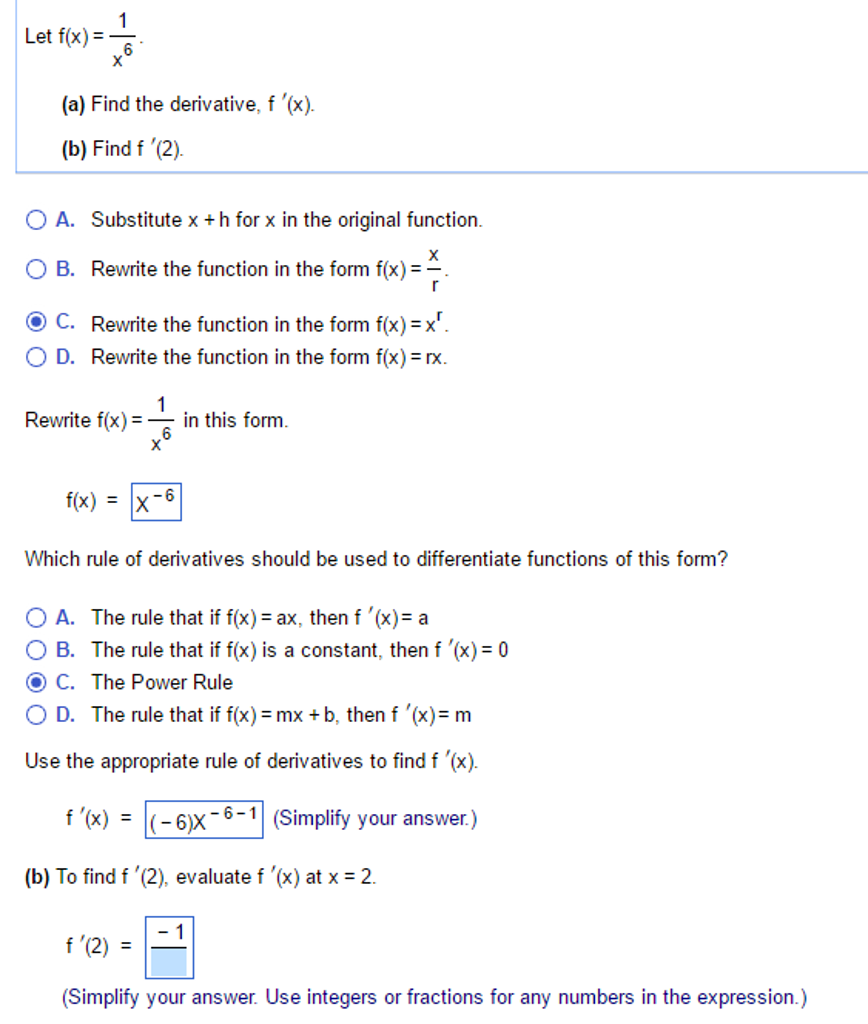



Let F X 1 X 6 Find The Derivative F X Find Chegg Com
f(x) = {(3x)/(1x)} 23x taking log on both sides log(fx) = (2 3x) log {(3x)/(1x)} log(fx) = (2 3x) log(3x) log(1x) Now differentiate f'(x) /f(x) = (2For instance, the first counterexample must be odd because f(2n) = n, smaller than 2n;F′′(x) = ∑∞ n=1 3n(3n−1)anx3n−2 = x {1 ∑∞ n=2 an−1x 3n−} = x {1 ∑∞ n=1 anx 3n} = xf(x) 812 10 8 6 4 2 0 2105 0 05 1 15 2 25 3 x y Figure 1 Graph of the Airy function f(x) = 1 ∑∞ n=1 anx 3n Remark Solutions of the ODE y′′ = xy are called Airy functions For x large and positive, they behave like exponential functions, and for x large and




How Do You Find A Quadratic Function F X Ax 2 Bx C For Which F 1 2 F 3 46 And F 3 16 Socratic



Http Smacmathapcalculus Weebly Com Uploads 1 9 2 5 Fc Unit 3 1 Hw Key V2 Pdf
Next Misc 3→ Chapter 2 Class 11 Relations and Functions (Term 1) Serial order wise;About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsClick here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If f(x) = (x 1)(x 1) then prove that f(2x) = 3f(x) 1f(x) 3




4 2 Linear Approximations And Differentials Mathematics Libretexts



Www Tamdistrict Org Cms Lib Ca Centricity Domain 3 12 Exam Solutions with detailed solutions Pdf
Miscellaneous Misc 1 Important Misc 2 You are here Misc 3 Misc 4 Important Misc 5 Misc 6 Important Misc 7 Deleted for CBSE Board 22 Exams Misc 8 Misc 9 Important Misc 10 Important Misc 11 Important Misc 12 Important Finding Cartesian Product → Facebook Whatsapp Transcript Misc 2 If f(xLog in Doruk I Numerade Educator Like Report Jump Explanation Given f (x) = 3x −2 Substitute x 1 for every x f (x 1) = 3(x 1) − 2 f (x 1) = 3x 3 −2




If F X X 1x 1 Then F 2x In Terms Of F X Is




Derivatives Of Inverse Functions From Equation Video Khan Academy
f(x) = x^3 x^2 x 1 f'(x) = 3·x^2 2·x 1 f''(x) = 6·x 2 a) Berechne die Nullstellen, Hoch und Tiefpunkte und den Wendepunkt des Graphen von f Skizziere anschließend den Graphen im Intervall I = 1,5; Ex 12, 10 Let A = R − {3} and B = R − {1} Consider the function f A → B defined by f (x) = ((x − 2)/(x − 3)) Is f oneone and onto?Crystinia crystinia Math Primary School If f(x) = x^3 x^2 x 1 Then the value of f ( 1 ) f ( 1 ) / 2 = _____ 2 See answers nd sry for saying u inappropriate things I will always be grateful to u Nd i assure u that i will help you in solving ur questions ^_^ ^_^ ^_^ ok



If F X 2f 1 X X 2 Then What Is F X Quora




If X 1 A N D F X X 1 X 1 Is A Real Function Then F F F 2 Is A 1 B 2 C 3 D 4
Join for Free Problem If $ g(x) x \sin g(x) = x^2, $ find $ g'(0) $ 0134 View Full Video Already have an account?2 1 0 1 2 x f(x) exp (x) 1 x 1 0 1 3 5 7 x f(x) log (1 x) x Wir appro ximieren exp (x) an der Stelle 0 durch eine Ger ade exp (x) = 1 x Wir appro ximieren log (1 x) an der Stelle 0 durch eine Ger ade log (1 x) = x Josef Le ydold c 06 Mathematische Methoden IX Taylorreihen 9 / 25 Anwendung Für alle x 2 R gilt lim n !F (x) = e x e x xe x = 2 e x xe x f(3)(x) =2 ex x xex 3 ·x x f(4)(x) = 4 e x xe f(5)(x) = 5 e x xe The inductive step in the proof of this for the general case looks like f(k)(x) = kex xex ⇒ f(k1)(x) = kex e x xe = (k x 1)e xe x 2 Find the equation of the tangent line to the "astroid" curve defined implicitly by the equation x 2/3 y 2/3 = 4 at the



If F X Log 1 X 1 X Show That F 2x 1 X 2 2f X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



F X 2x2 3x X 2 If X 2 At X 2 If X 2 Studyrankersonline
If `f^2(x)*f((1x)/(1x))=x^3, x!=1,1 and f(x)!=0,` then find `f(2)` (where is the greatest integer function)Select a few x x values, and plug them into the equation to find the corresponding y y values The x x values should be selected around the vertex Tap for more steps Replace the variable x x with − 2 2 in the expression f ( − 2) = ( − 2) 2 2 ( − 2) − 1 f ( 2) = ( 2) 2 2 ( 2) 11x 2 3(1x)3=2 C 2) Partielle Integration Seien f(x) und g(x) stetig difierenzierbar auf einem Intervall I Dann gilt R f(x)g0(x)dx = f(x)g(x) ¡ R f0(x)g(x)dx (wobei "=" so zu verstehen ist, dass sich linke und rechte Seite nur um eine Konstante unterscheiden) Beweis Aus der Stetigkeit von f0(x) und g0(x) folgt mit dem 1 Hauptsatz der Difierential und Integralrechnung, dass f(x)g0(x
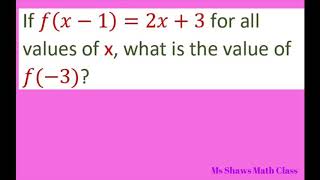



If F X 1 2x 3 Find F 3 Youtube



Web Stanford Edu Class Archive Math Math41 Math41 1142 Oldexams 09finalsol Pdf
Tabelle einfacher Ableitungs und Stammfunktionen (Grundintegrale) Diese Tabelle ist zweispaltig aufgebaut In der linken Spalte steht eine Funktion, in der rechten Spalte eine Stammfunktion dieser FunktionDie Funktion in der linken Spalte ist somit die Ableitung der Funktion in Given, f(x) = (x 1) 3 (x 2) 2 On differentiating both sides wrt x, we get Now, we find intervals and check in which interval f(x) is strictly increasing and strictly decreasing



Math Scene Equations Iii Lesson 3 Quadratic Equations




If F X 2f 1 X 3x X 0 And S X In R F X F X Then S 1 Is An Empty Set 2 Contains Exactly One Element 3 Contains Exactly Two Elements 4 Contains More Than Two



Q Tbn And9gcq3k4crna5aowbckdwotcepc7srb Ubkhdcqsvwzwhqp8plminb Usqp Cau



Math Scene Equations Iii Lesson 3 Quadratic Equations
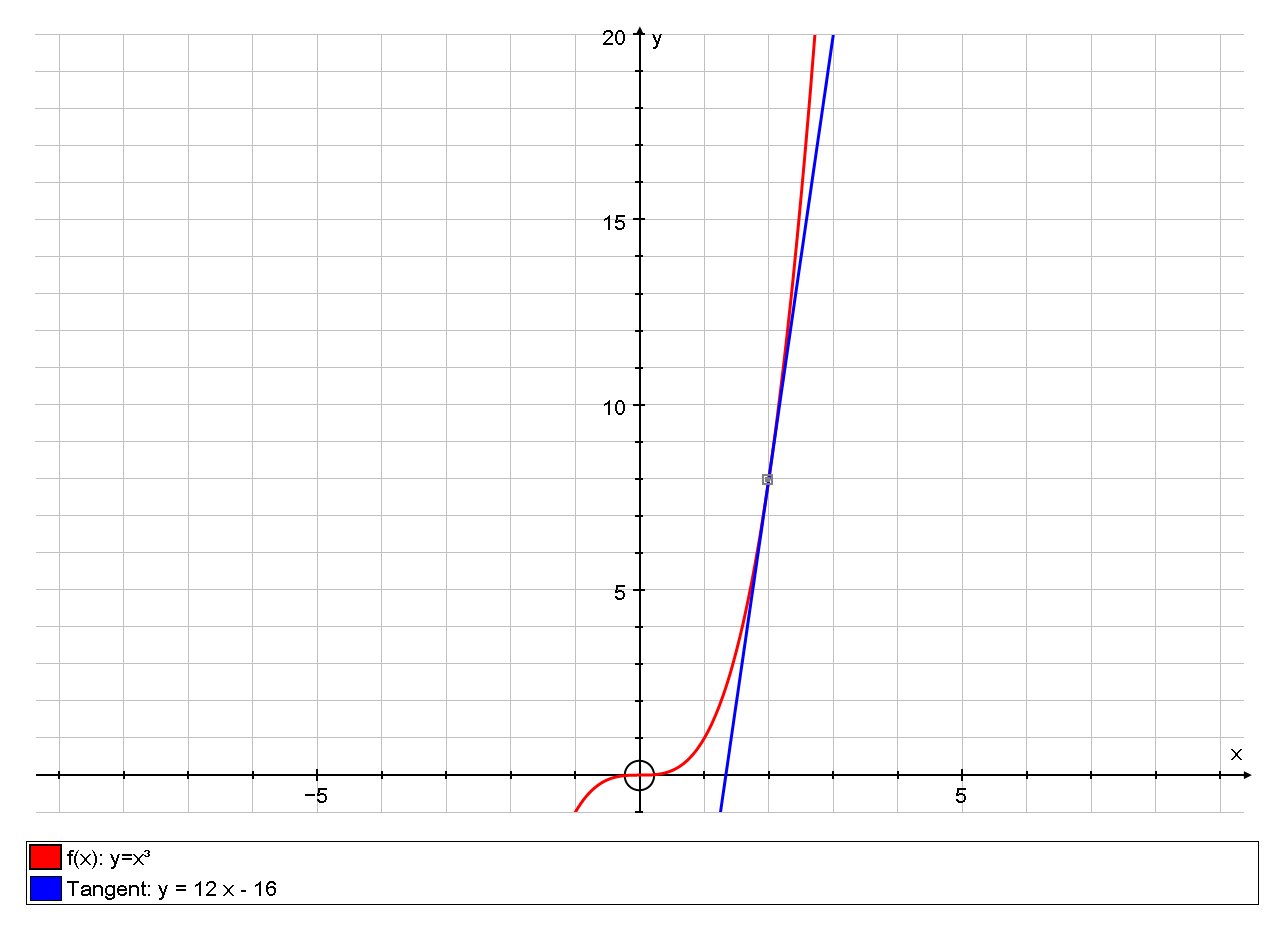



How Do You Find The Equation Of The Tangent Line To The Graph Of F X X 3 At Point 2 8 Socratic



F 1 X F X 1 What Is The Name Of This Functional Equation And In Biconditional Form



If Math F 2x 1 X Math What Is Math F 2 Math Quora




Ex 1 2 1 Class 12 Maths Show F X 1 X Is One One Onto Where R




If 2f X 3f 1 X X 2 1 Then F X Is Youtube




Ex 1 2 10 F X X 2 X 3 Is F One One Onto Class 12




If F X 2 X 2 5 1 Find F 1 X F 1 X 5 Chegg Com



Math Scene Functions 2 Lesson 6 Inverse Functions



1




A Function F X Satisfies The Functional Equation X 2f X F 1 X 2x X 4 For All Real X F X Must Be



Http Library Abes Ac In E Books Engineering mathematics iii module 4 2 Pdf
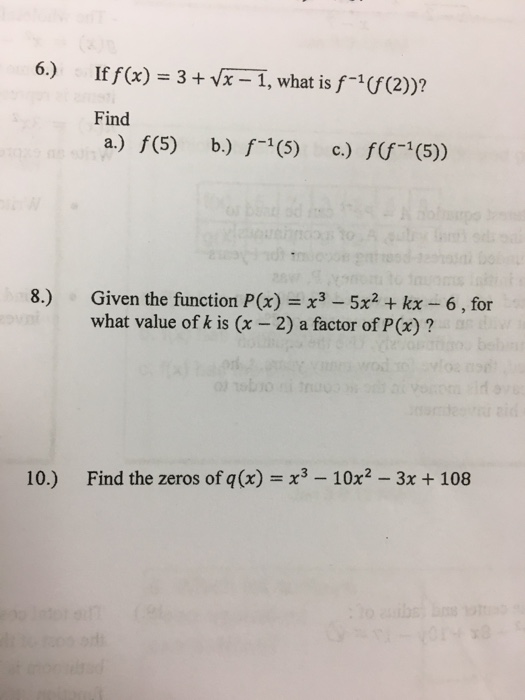



If F X 3 Squareroot X 1 What Is F 1 F 2 Chegg Com




If F X F Xf Xf X Where F 1 2 F 2 3 F 1 4 F 2 5 And F 3 6 How Do You Find F 1 Brainly In




If F X X 1 X Prove That F X 3 F X 3 3f 1 X Brainly In



If F X Cos X Then How Can We Show That F 2x 2 F X 2 1 Is Equal Quora



Www Tamdistrict Org Cms Lib Ca Centricity Domain 3 12 Exam Solutions with detailed solutions Pdf



Projecteuclid Org Download Pdf 1 Euclid Kjm




If F X X3 1 X3 Prove That F X F 1 X 0 Brainly In




Example 10 If F 1 X X 1 Then Find F 2 H Substitute X 1 H In Given Function And Get The Value Of F 2 H Sol We Have F 1 X




Verifying Inverse Functions By Composition Not Inverse Video Khan Academy




Using The Definition Of The Derivative Find F X Chegg Com



If F X Log 1 X 1 X Then What Is F A F B Equal To Quora




Find The Domain And Range Of The Function F X 1 1 X 2 X In R X 1 Dot




Example 12 Show That F X X 1 If X Is Odd X 1 If X Is Even




Consider F R 4 3 R 4 3 Given By F X 4x 3 3x 4 Show That F Is Bijective Find The Inverse Of F And Hence Find F 1 0



1




If G X Is The Inverse Function Of F X And F X 11 X 4 Then G X Is



Www Ebnet Org Cms Lib Nj Centricity Domain 816 Answer key ii Pdf
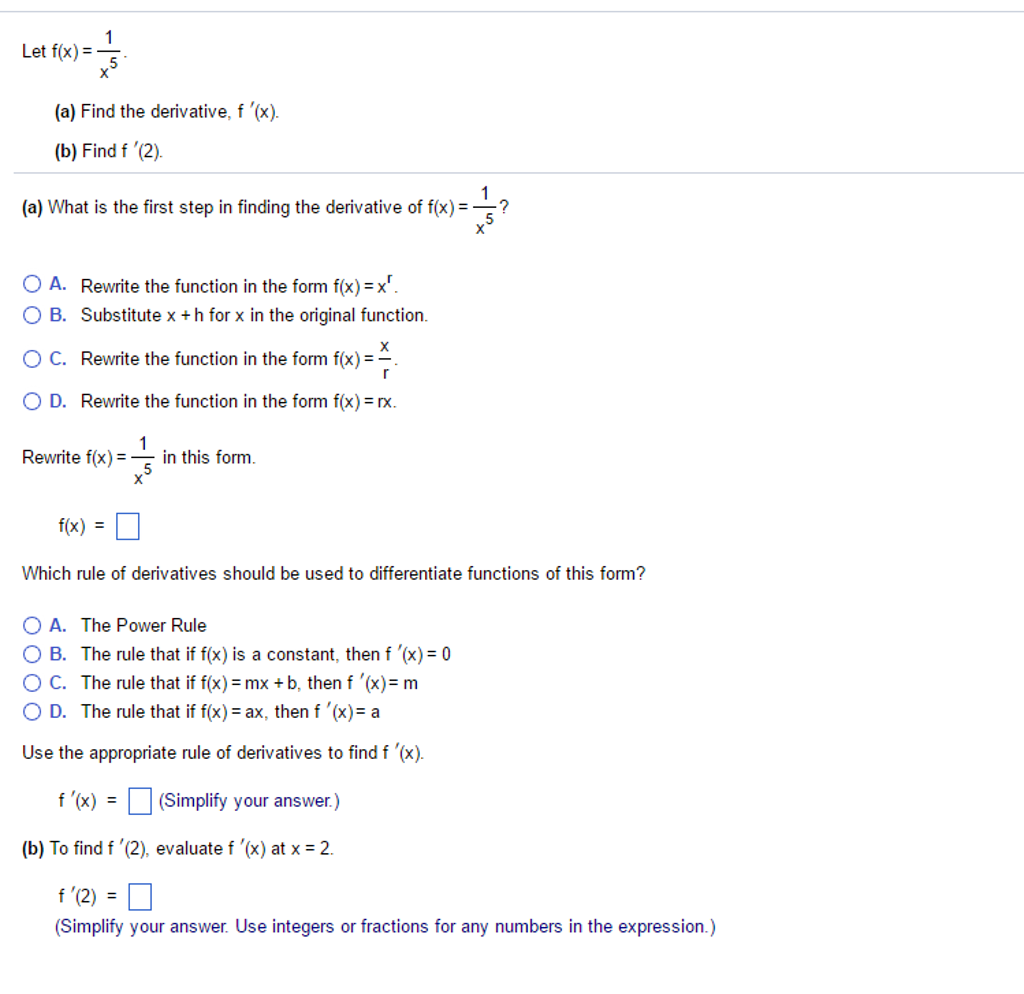



Let F X 1 X 5 A Find The Derivative F X Chegg Com
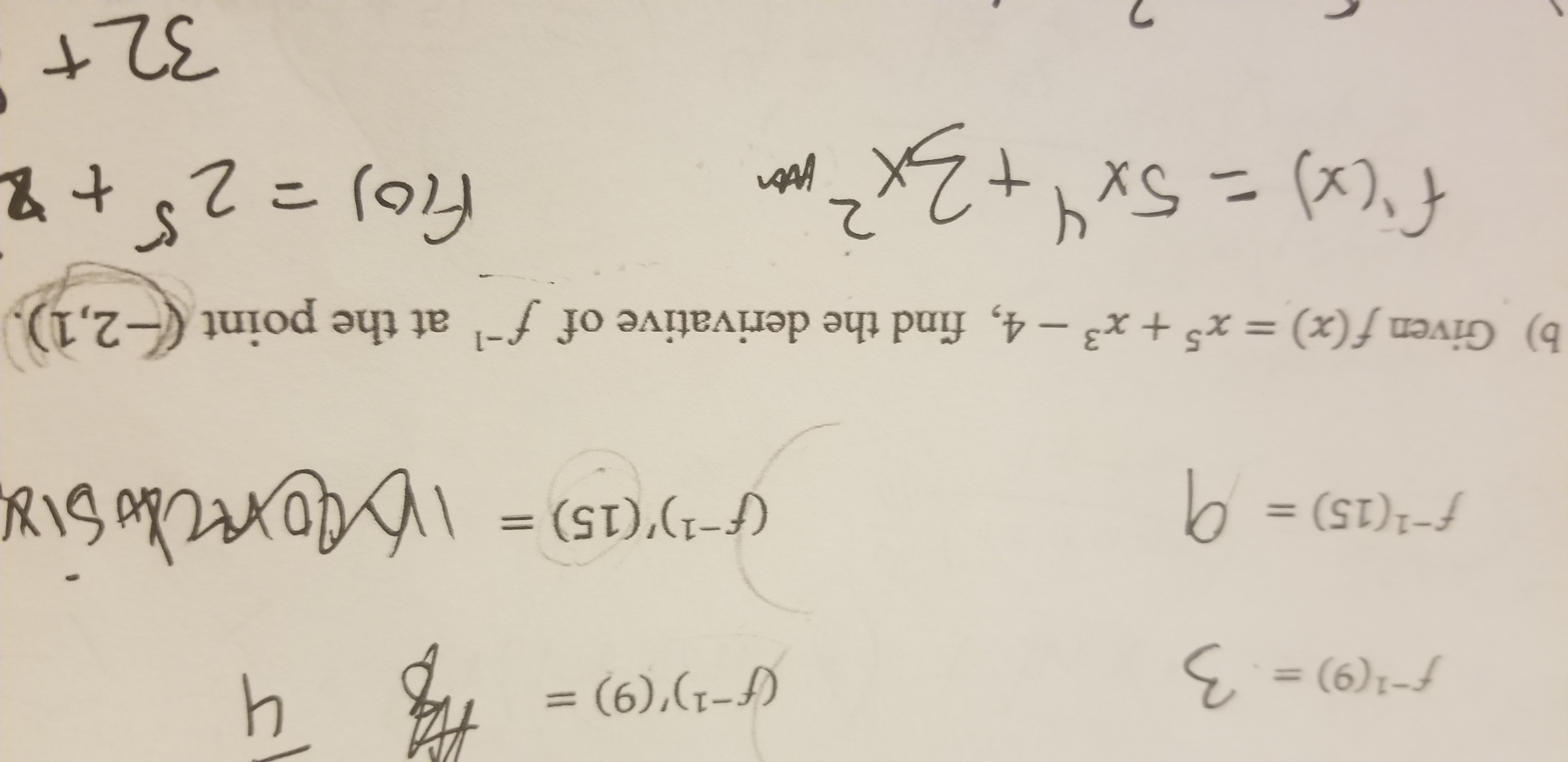



Answered 41 9 3 F1 9 F 15 0 Bartleby



Uncw Edu Ulc Services Math Documents Mat 111 Final Exam Answer Key Sp17 Pdf




If F 2 X F 1 X1 X X 3 X 1 1 F X 0 Then Find F 2 Where Is The G I F




Ex 1 2 10 F X X 2 X 3 Is F One One Onto Class 12




If F X X 1 X 1 Then Show That F 1 X F X Ii F 1 X 1 F X




How To Determine If A Function Is One To One Mathematics Stack Exchange




F X Sin A 1 X Sinx X X Lt 0 C X 0 Root Of X Bx 2 Root Of X Bx 3 2 X Gt 0 Mathematics Topperlearning Com 5gbkb9bb
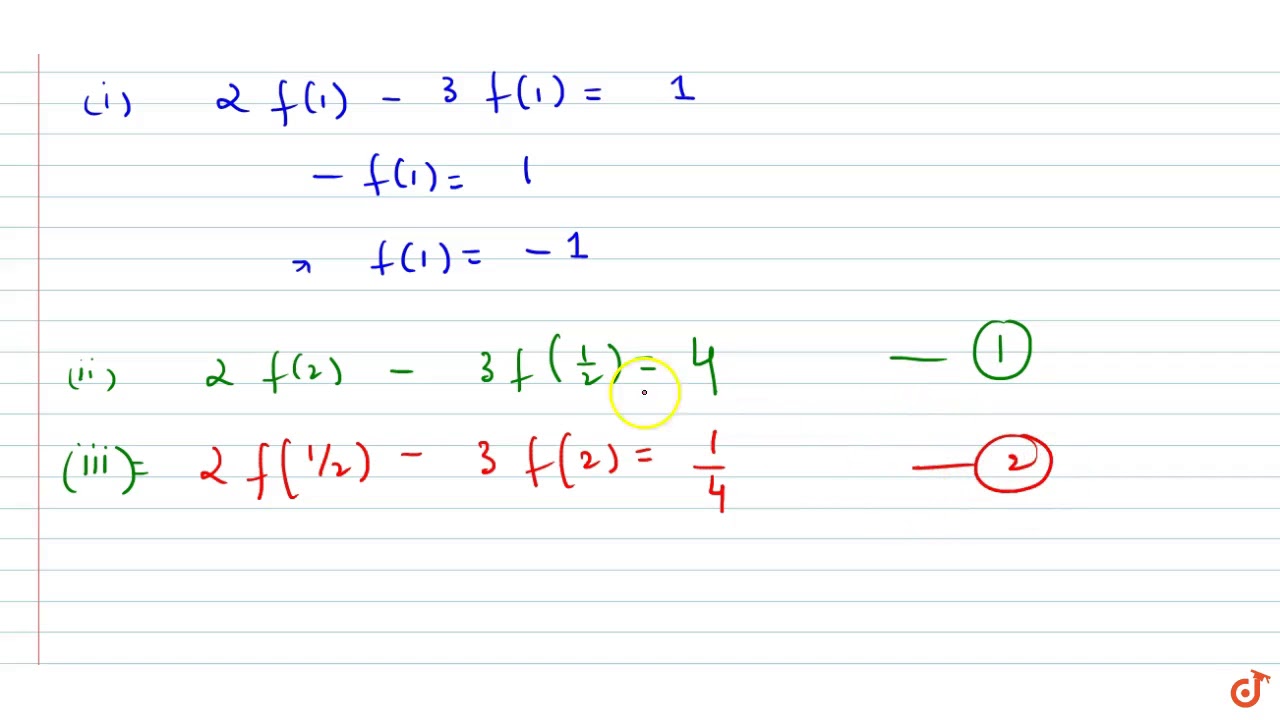



If 2f X 3f 1 X X 2 X 0 Then F 2 Is Equal To 7 4 B 5 2 C 1 D None Of T Youtube




If F X Log 1 X 1 X Then F 2x 1 X 2 Is Equal To




Ex 7 1 22 Mcq If F X 4x3 3 X4 F 2 0 Then F X Is



Www Tamdistrict Org Cms Lib Ca Centricity Domain 3 12 Exam Solutions with detailed solutions Pdf



Www3 Nd Edu Apilking Math Work Old exams Exam 3f12 Sols Pdf
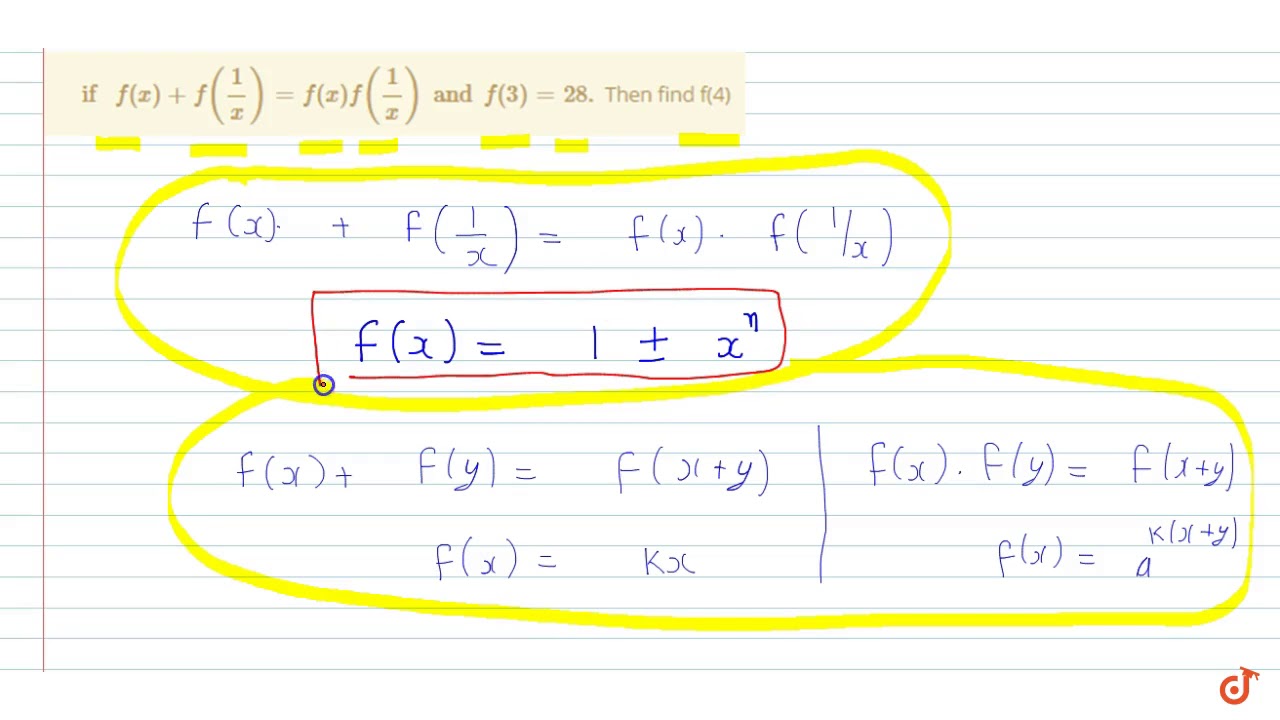



If F X F 1 X F X F 1 X And F 3 28 Then Find F 4 Youtube




If The Function F R R Defined By F X 4 X4 X 2 Then Show That F 1 X 1 F X And Hence Deduce The Value Of F 14 2f 12 F 34



Www Math Utah Edu Wortman 1050 Text If Pdf




If F X 9 X Upon 9 X 3 Then F X F 1 X Brainly In




If F X Log 1 X 1 X Then Show That F X F Y F X Y 1 Xy Brainly In



If F X Is A Polynomial Satisfying F X F 1 X F X F 1 X And F 3 28 Then F 4 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Madasmaths Com Archive Maths Booklets Standard Topics Various Function Exam Questions Pdf



Composition Of Functions Composing Functions At Points



F 1 X F X 1 What Is The Name Of This Functional Equation And In Biconditional Form



Www Herricks Org Cms Lib Ny Centricity Domain 290 Winter review packet solutions Pdf



Free Essays Homework Help Flashcards Research Papers Book Reports Term Papers History Science Politics




If F X F 1 X F X F 1 X And F 3 28 Then Find F 4
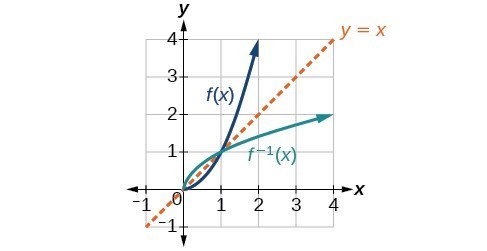



Use The Graph Of A Function To Graph Its Inverse College Algebra



Let F X X 2 Ax B If For All Nonzero Real X F X 1 X F X F 1 X And The Roots Of F X 0 Are Integers What Is The Value Of A 2 B 2 Quora



If F X 3x 2 And Gof 1 X 2 Then Find The Function Of G X Youtube



Let A R 3 B R 1 If F A B Be Defined By F X X 2 X 3 X A Studyrankersonline
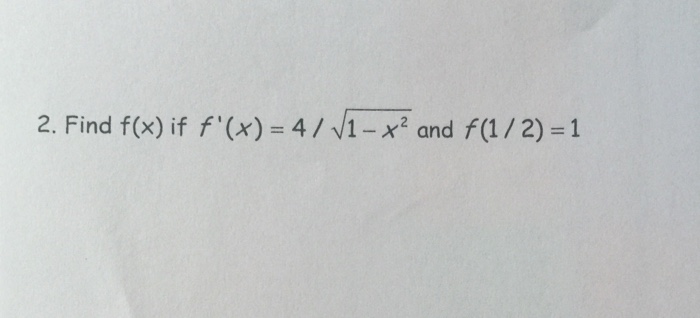



Find F X If F X 4 Square Root 1 X 2 And F Chegg Com



Graphing Types Of Functions




Find The Value Of A And B Such That The Function Is Continuous At X 0 F X X Sin X Sin A 1 X If 3w7glx22 Mathematics Topperlearning Com




If A Function F R R Be Defined By F X 3x 2 X 0 1 X 0 4x 1 X 0 Find F 10 F 1 F 0 F 2 Dot



How To Solve F X Log 1 X 1 X And Then F 2x 1 X 2 Quora




If F X X 1 X And F 1 5 2 Then F X Brainly In




If F X X 3 X 2f 1 Xf 2 F 3 Then F 2 Is A 2 B 1 C 30 D 2




If F X X 1 X 1 Then F 2x Is Equal To



Search Q Graph Transformations Tbm Isch



Let F R R Be A Function Such That F X X 3 X 2 F 1 Xf 2 F 3 X R Then F 2 Equals Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Madasmaths Com Archive Maths Booklets Standard Topics Various Function Exam Questions Pdf



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Apcentral Ap15 Calculus Ab Q2 Pdf
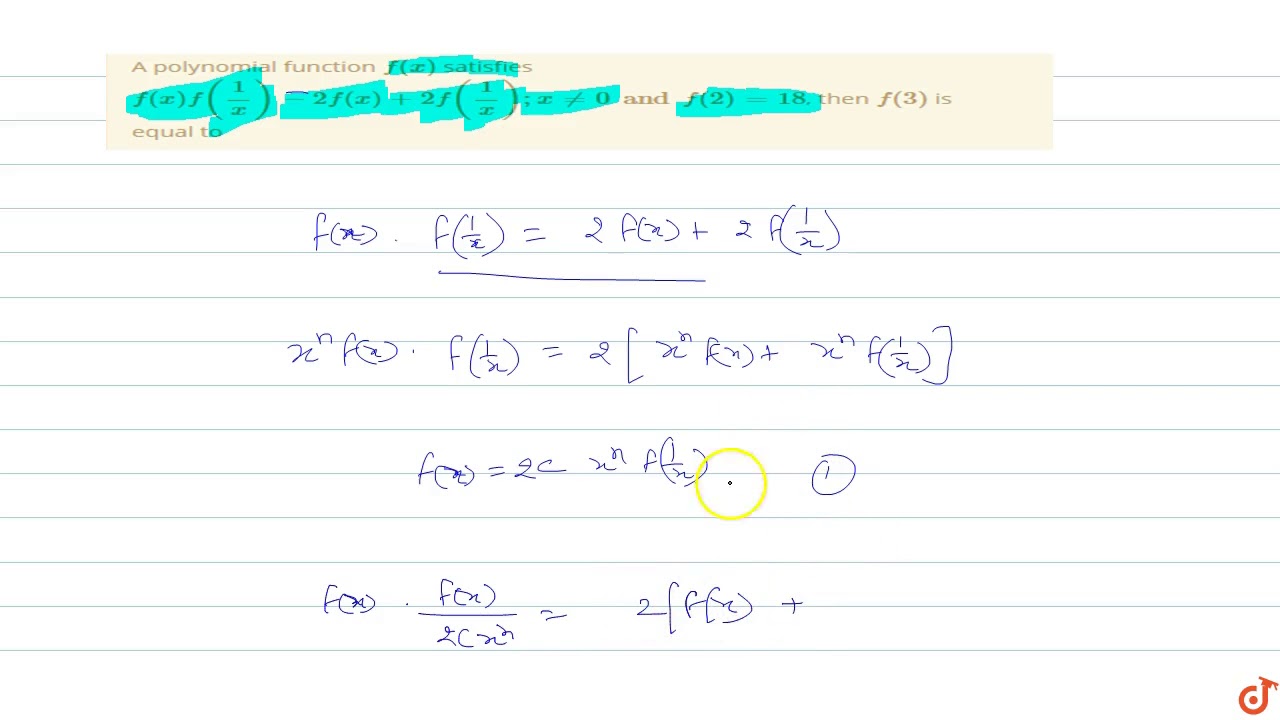



A Polynomial Function F X Satisfies F X F 1 X 2f X 2f 1 X X 0 And F 2 18 Then Youtube



Www Alvinisd Net Cms Lib Tx Centricity Domain 436 Math 1314 61 quiz solutions Pdf



If F X 2f 1 X 3x X 0 And S X R F X F X Then S Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿